With the arrival of 5G, all aspects of the mobile phone are more stringent requirements, of which battery life is undoubtedly a crucial link.
In addition to bigger and bigger batteries, higher and higher charging power is also a priority.
In the first few years of the development of smart phones, although mobile phone charging has been developing, its existence has been very low.
No wonder, because the battery capacity at the time was already small, and the overall experience of charging the phone did not directly improve the performance, camera pixel increase, so it was understandable.
But now, mobile phone fast charging has undoubtedly stood in the whole experience of the mobile phone in the C bit.
So today, let’s talk about the history of mobile phone charging.
(Let’s skip the feature phone era and start directly with the smartphone era, while wireless charging is not covered in this article.)
Although mobile phone charging seems to be a relatively small category, it is still very complicated to tell the need to involve voltage and current, various charging agreements and so on, so it is as simple as possible.
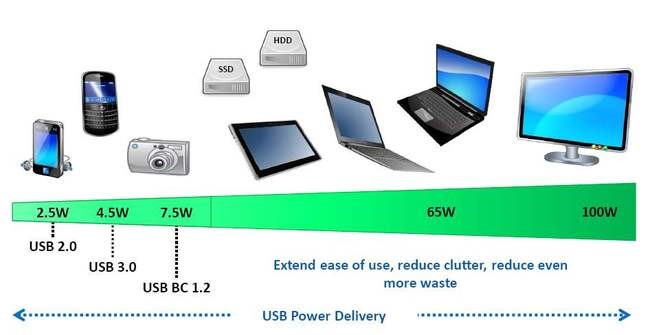
Strictly speaking, fast charging for smart phones started with USB BC 1.2 issued by USB IF in 2010. Its emergence not only standardized the chaotic situation of USB charging specification at that time, but more importantly, it increased the charging current to 1.5A, and the maximum power of USB charging interface reached 7.5W, which was enough to meet the charging demand at that time.
(Consider that Apple only dropped the 5V1A charging point out of the box last year…)
With the development of time, the battery capacity gradually increases, and the power consumption of the mobile phone also increases. At this time, USB BC 1.2 can no longer meet the charging demand of the mobile phone, but the USB IF still does not move, Qualcomm can not sit still.

In 2013, it broke the 1.5A limit of USB BC 1.2, increased the charging current to 2A, and reached the maximum charging power of 10W.
This was the original QC 1.0, heralding the arrival of the Qualcomm Quick Charging Protocol.
With the advantages of chip and communication, Qualcomm QC fast charge protocol has been rapidly popularized and expanded in Android phones.
From this point on, the development of mobile phone fast charging entered a fast track, and at the same time entered a chaotic period.
Qualcomm QC, MediaTek PE and manufacturers’ self-developed quick charge such as OPPO VOOC flash charge, Apple, Samsung AFC, Huawei FCP/SCP and so on.
Mobile phone charging is in accordance with P (power) =U (voltage) ×I (current), so the method to improve power is nothing more than to increase the voltage or current and the dynamic increase of both.
Qualcomm QC1.0 is to improve the charging power by increasing the current.
However, charging a phone isn’t just about the charging head, it’s also about the cable.
In 2014, when Qualcomm tried to increase the current along the QC1.0 direction to increase the charging power, it found itself stuck.
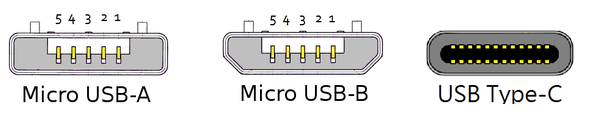
At this time, although Type-C data line has been released, it is still far from universal. Everyone is using MicroUSB 2.0 data line. Its internal structure results in its limited carrying capacity for current, and 2A is basically at an end.
So instead, Qualcomm raised the voltage to increase the charging power, which is called QC2.0.
Three quarters of millet have adopted the QC2.0 protocol.
Qualcomm QC2.0 directly increases the charging voltage from 5V to 9V/12V/20V, and 20V is mainly reserved for laptops.
So when the current is 2A, the charging power reaches 18W, while when the voltage is 12V, the current is only 1.5A, effectively reducing the current.
The advantage of QC2.0 is that it has low requirements for charging wires, so the cost is low, and the disadvantage is that the charging heat is low and the efficiency is low.
At this time, OPPO went the opposite way of Qualcomm, namely, low voltage and large current.

Since the ordinary wire can not withstand such a large current, so Oppo directly from the charging head to the data line for a complete transformation.
The number of contacts in the normal microUSB is increased to 7, and the charging head is integrated with an IC circuit.
To build from the adapter to the interface to the mobile phone of the whole end of the five-fold protection technology.
Such a big deal and depth of transformation makes the initial VOOC flash charge directly to 5V5A25W, with a “charging 5 minutes, talk 2 hours” slogan, OPPO VOOC flash charge the world knows.
The advantages are small heating, high charging efficiency and fast charging;
The disadvantage is no doubt that the cost is high, only support the compatibility of OPPO’s own products.

In 2015, Qualcomm released QC3.0, which is mainly based on the addition of INOV optimal voltage intelligent negotiation algorithm. 200mV is a set voltage, the lowest voltage can be lowered to 3.6V and the highest voltage can be lowered to 20V, providing a flexible choice of voltage from 3.6V to 20V, and it is compatible with QC2.0 downward.
Moreover, due to the popularity of Type-C interface at this time, the maximum charging current is also increased to 3A.
Therefore, QC3.0 allows portable devices such as mobile phones to get just the right voltage and the desired current to minimize power loss, improve charging efficiency and improve thermal performance.
Qualcomm says it’s up to a 38% increase in efficiency, a 27% increase in charging speed and a 45% reduction in heat.

Moreover, due to the popularity of Type-C interface at this time, the maximum charging current is also increased to 3A.
Therefore, QC3.0 allows portable devices such as mobile phones to get just the right voltage and the desired current to minimize power loss, improve charging efficiency and improve thermal performance.
Qualcomm says it’s up to a 38% increase in efficiency, a 27% increase in charging speed and a 45% reduction in heat.

Therefore, USB IF released the charging standard of USB Power Delivery (referred to as USB PD) based on the Type-C interface in USB 3.1, which can provide the highest charging Power of 100W (20V/5A), aiming to unify the charging standard of portable mobile devices.
And everyone can obediently listen to their own charging protocol into the USB PD protocol, in addition to USB IF are the industry leaders, Google also said that Android must support USB PD.
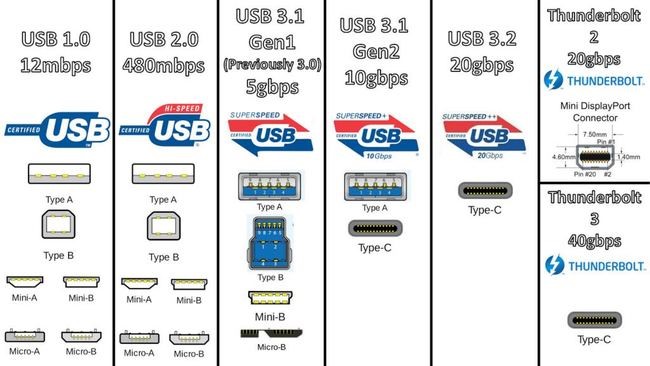
The 2017 USB PD3.0 is compatible with Qualcomm QC4.0/3.0, Oppo VOOC, Huawei FCP/SCP, etc., and covers the high voltage low current and low voltage high current. The voltage output range is 3.0V-20V, the voltage adjustment range is 20mV, and the current range is 1.5A, 2A, 3A, 5A.
In 2017, Qualcomm released QC4.0+, which improved dual power management IC, intelligent heat balance, advanced safety features and so on.
At the same time, compatible with USB PD 3.0 (PPS) protocol and downward compatible with PD2.0, QC3.0, QC2.0 and so on.
After the PD3.0 agreement, means to develop a set of standards, everyone should follow this standard, OPPO VOOC flash charge is no exception.

Oppo VOOC flash charge has always been the representative of low voltage and large current, and today it has also developed from the original VOOC1.0 to VOOC4.0 (30W).
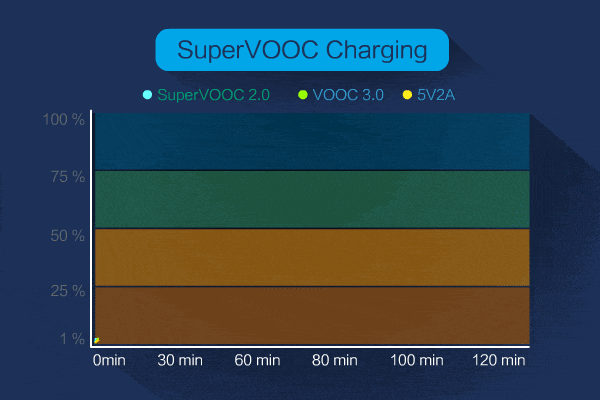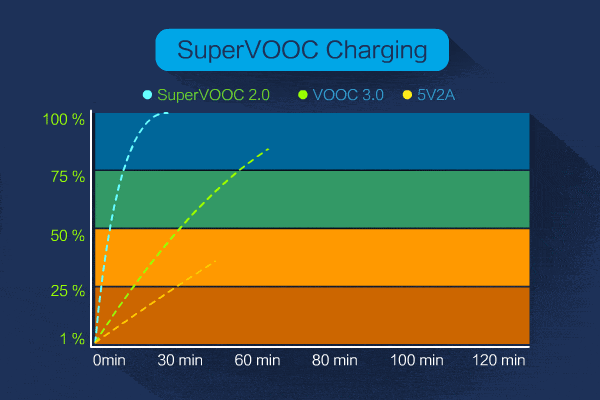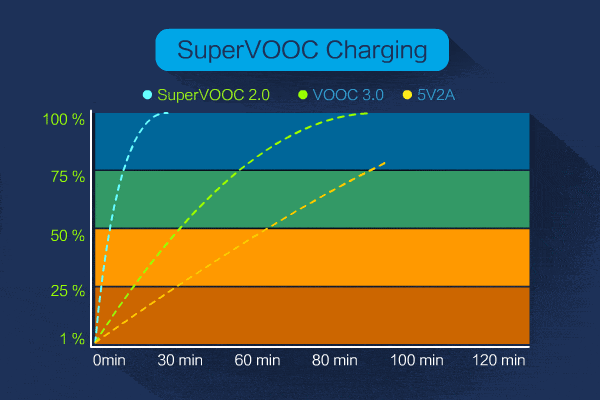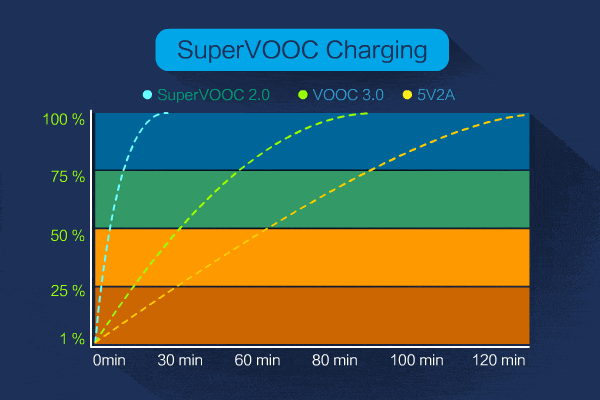
There is also an updated version of SuperVooc, up from nearly 50 watts of charging power for the original SuperVooc 2.0 to 65 watts, which is already in commercial production.
There is also a 30W wireless VOOC flash charge.
At present, what we can get access to is SuperVooc 2.0 65W flash charge, of course, Xiaomi’s 100W and even Vivo’s 120W are still on the way, I believe we can basically use it in the second half of this year and next year at the latest.